Wie funktioniert das Immunsystem? Lerne es zu verstehen und beeinflussen.
Der Einfluss unserer Lebensweise und vor allem der Ernährung hat einen entscheidenden Einfluss auf unsere Stoffwechselprozesse. Dazu zählen nicht nur die Verdauung wie die Zersetzung und Aufnahme von Nährstoffen, sondern auch die vielen anderen Prozesse die jede Sekunde in unserem Körper stattfinden. Jede Sekunde werden neue Blutkörper gebildet und alte recycelt. Wir verlieren tausenden an Hautzellen, welche sich wieder neu regenerieren. Muskelzellen werden repariert, die Haare und Nägel wachsen und vieles mehr.
Wie funktioniert das Immunsystem?
Der Körper befindet sich in einem ständigen Balanceakt zwischen Tod und Erschaffung neue Zellen, Hormone und Gewebe.
Zu diesen Stoffwechselprozessen gehören auch alle Prozesse rund um das Immunsystem. Trotz tausender Forschungsarbeiten und Studien sind längst noch nicht alle Geheimnisse um das komplexe Zusammenspiel der Immunprozesse entschlüsselt.
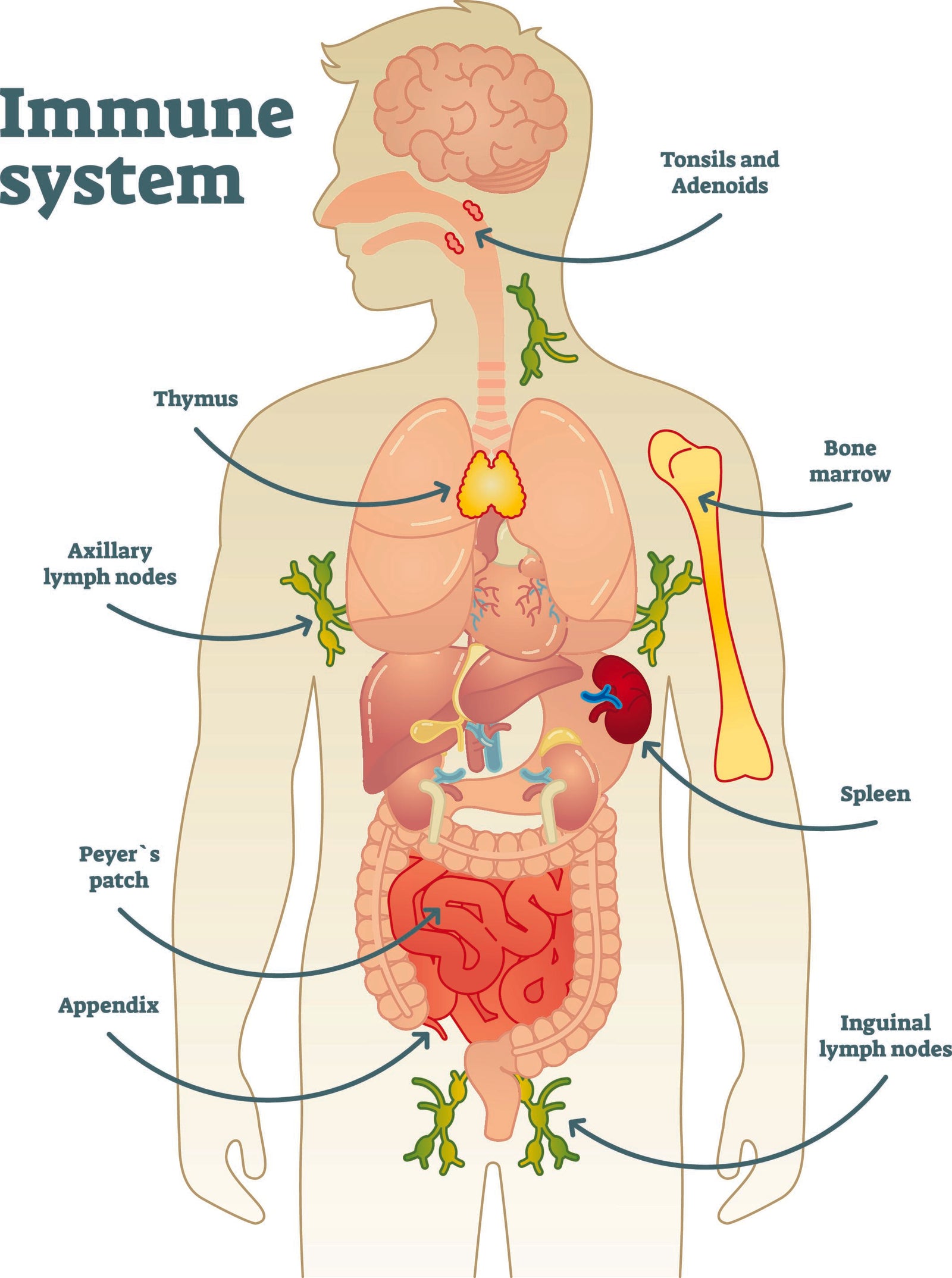
Für seine Funktionsweise benötigt unser Immunsystem ein komplexes Gebilde aus immunkompetenten Systemen, dazu gehören:
- das Knochenmark
- der Thymus
- die Lymphknoten
- die Milz
- die Haut
- der Darm und die Darmflora
- spezialisierte Immunzellen und Botenstoffe im Blut
Die Aufgaben des Immunsystems
Das Immunsystem hat ganz spezifische Aufgaben im Körper, darunter zählen:
- Aufrechterhalten von natürlichen Barrieren (Haut, Darmwand)
- Screening auf Fremdkörper
- Abwehrreaktionen einleiten
- Erkennen und abtöten von mutierten Zellen
- Immungedächtnis verwalten
Um all diese Aufgaben zu meistern, besteht unser Immunsystem aus zwei Teilen. Das unspezifische Immunsystem und das spezifische Immunsystem.
Das unspezifische Immunsystem besteht aus natürlichen Barrieren (Haut, Darmwand) und einem Netz von Abwehrzellen, die alles, was fremd ist und einem gewissen Muster zugeordnet werden kann, angreift respektive das Eindringen in den Körper verhindert.
Das spezifische Immunsystem besteht aus anpassungsfähigen und lernfähigen Zellen. Es wird vom Thymus gesteuert welches mithilfe der Fresszellen eine immunspezifische Antwort auf einen Einfall von schädlichen Fremdkörpern einleitet. Dies passiert beim Befall von Grippeviren, hier stellt der Körper neue Immunkörper her, welche gezielt diese Grippeviren neutralisieren. Dieser Prozess kann jedoch einige Tage in Anspruch nehmen. Auch über die Grippe hinaus bleiben diese Zellen im Körper enthalten und schaffen so eine Art Memory Effekt der über Wochen bis hin zu einigen Jahren anhalten kann. Bei einem erneuten Befall mit dem gleichen Fremdkörper, kann das Immunsystem nun blitzschnell reagieren.
Es ist wichtig, dass das Immunsystem stets im Gleichgewicht ist, eine überschießende oder ungenügende Immunreaktion ist nicht erwünscht.
Erkrankungen des Immunsystems
Auch unser Immunsystem selbst kann Fehlfunktionen und Störungen besitzen, es ist dann selbst krank oder aus dem Gleichgewicht. Dabei können viele Faktoren sich auf das Immunsystem positiv oder auch negativ auswirken:
- Lebensweise (Stress, wenig Schlaf, Bewegungsmangel, Elitesport)
- Medikamente (Antibiotika, Schmerzmittel, Impfungen, Hormontherapien)
- Infektionen (Bakterien, Viren, Pilze)
- Umweltgifte (Schwermetalle, Pestizide, chemische Substanzen)
- Ernährung (Überernährung, Unterernährung, Fehlernährung)
- Genussmittel (Drogen, Alkohol, Tabak)
- Zusatzstoffe (Emulgatoren, Geschmacksstoffe, Farbstoffe)
- physikalische Belastungen (Elektrosmog, Strahlung)
Die Studien bezüglich des Einflusses der Umweltfaktoren und übertriebener Hygiene sind noch nicht eindeutig. Fest steht jedoch, dass auch diese das Immunsystem beeinflussen. Bei Allergien reagiert das Immunsystem auf tägliche Fremdkörper wie die Pollen beim Heuschnupfen. Bei Autoimmunkrankheiten bekämpft das Immunsystem irrtümlicherweise eigene Körperzellen.
Wie stärke ich mein Immunsystem
Das Immunsystem kann nur optimal funktionieren, wenn es auch mit den nötigen Nähr- und Baustoffen versorgt wird. Hierfür ist eine vollwertige und ausgewogene gesunde Ernährung der Schlüssel. Aber auch genügend Ruhe und Erholung sind von ausschlaggebender Bedeutung.
"Sleep affects various immune parameters, is associated with a reduced infection risk, and can improve infection outcome and vaccination responses." The Sleep-Immune Crosstalk in Health and Disease. 2019 Jul 1;99(3):1325-1380
Wichtige Faktoren bei der Auswahl der Lebensmittel sind, dass diese vor allem so naturbelassen wie möglich sein sollten. Frisches Obst und Gemüse sind reich an Vitaminen, Mineralstoffen und auch sekundären Pflanzenstoffen.
Auch frische hochwertige Öle und eine ausgewogene Aminosäure Bilanz unterstützen das Immunsystem und sind wichtig für eine optimale Funktionsweise.
Wie wichtig eine gesunde Ernährung auf den Körper und das Immunsystem ist, erkannte schon vor mehr als 2000 Jahre der griechische Gelehrte Hippokrates.
"Let food be thy medicine and medicine be thy food", Hippokrates 460 v. Chr.
Hippokrates vertrat die Auffassung: "Die Gesundheit kann nur durch eine richtige Mischung der Körpersäfte, die natürlich sehr von der Ernährung und einer natürlichen Lebensweise abhängen, erhalten werden. Eine fehlerhafte Mischung der Körpersäfte stört die Lebensharmonie und damit das Gleichgewicht im Körper."
Hygiene und das Immunsystem
Die Hygiene ist vor allem für das vorher genannte unspezifische Immunsystem von Bedeutung. Eine ausgewogene Körperhygiene kann die natürliche Barriere, unsere Haut, unterstützen und somit das Eindringen von bösartigen Fremdkörpern reduzieren.
Wichtig ist vor allem die Hygiene im Intimbereich, denn dort befinden neben Mund, Ohren und Nase weitere Eingangstore in innere unseres Körpers.
Auch bei der Hygiene kommt es auf ein gesundes Maß an, so kann übermäßige Hygiene auch dem Immunsystem die Fähig nehmen, sich an neue Situationen und Erreger anzupassen. Zudem kann übermäßiges Duschen (mehrmals am Tag) die natürliche Schutzbarriere der Haut zerstören.
Immunsystem unterstützende Ernährung
Wie bereits im vorherigen Kapitel erwähnt, ist eine gesunde und ausgewogenen Ernährungsweise essenziell um das Immunsystem optimal zu unterstützen. Was versteht man jedoch unter einer gesunden Ernährungsweise?
Hier einfache 8 Regeln die du beachten solltest:
- Esse täglich 4-6 Portionen frisches Obst und Gemüse.
- Achte darauf genügend Ballaststoffe zuzuführen (min 30gr/Tag).
- Bevorzuge komplexe Kohlenhydrate aus Vollkorn- und stärkehaltigen Lebensmitteln (Kartoffeln, Reis).
- Esse nicht mehr Kalorien, als du täglich benötigst.
- Bereite deine Speisen nährstoffschonend zu (nicht verbraten).
- Gesundheitsfördernde Fette nutzen (Omega-3 und Omega-6).
- Nutze tierische Nahrungsmittel zur Nährstoffergänzung.
- Trinke genügend Wasser.

Einfluss von Sport auf das Immunsystem
Neben einer gesunden und ausgewogenen Ernährung, spielt auch unsere körperliche Aktivität eine essenziell, um das Immunsystem optimal zu unterstützen. Sport fördert wichtige Hormone und Stoffwechselprozesse und hilft dem Körper vital zu bleiben. Sport im Freien wirkt sich positiv auf unsere Sauerstoffzufuhr und Vitamin D spiegel aus. Vitamin zählt als eines der immunrelevanten Vitamine.
Studienergebnisse zeigen günstige Effekte eines moderaten Ausdauertrainings auf die Funktionalität des Immunsystems.
Bei moderater sportlicher Aktivität konnten in Trainingsstudien eine Verbesserung der Aktivität des Immunsystems festgestellt werden.
Immunoseneszenz ist definiert als eine Immundysregulation mit dem Alterungsprozess. Neuere Daten belegen, dass gewohnheitsmäßige Bewegung die Regulierung des Immunsystems verbessern und den Beginn der Immunoseneszenz verzögern kann.
Wiederholte, schwere Trainingseinheiten wie man sie oft bei Elitesportlern findet, wirken sich dagegen negativ auf das Immunsystem aus. So können andauernde schwere Belastungen Infektionen und Entzündungsprozesse Fördern.

Die Rolle der Darmflora
Eine wichtige Rolle für das Immunsystem spielt das sogenannte Mikrobiom, auch Darmflora genannt. In unserem Darm leben Milliarden von Bakterien welche mit unserem Körper in einer einzigartigen Weisen interagieren. Eine ballaststoffreiche Ernährung hilft hier die Darmflora und vor allem die gesunden Bakterien zu unterstützen.
Den Einfluss der Darmflora auf unser allgemeines Wohlbefinden wird derzeit intensivst erforscht. Er ist viel grösser als viele erwartet hätten.
Sie sorgen für eine funktionierende und fremdkörper-abweisende Darmwand. Durch die optimierte Aufnahme von Nährstoffen über die Darmwand und das Neutralisieren von böswilligen Bakterien spielt die Darmflora eine entscheidende Rolle als Teil des Immunsystems.
Die Rolle der Mikronährstoffe
Die richtige Zufuhr an Mikronährstoffen, dazu zählen vor allem Vitamine, Spurenelemente und sekundäre Pflanzenstoffe sind essenziell für ein gesundes Immunsystem. Hier spielt wiederum der Aspekt einer gesunden Ernährung und Lebensweise eine entscheidende Rolle.
Die richtige Balance an Mikronährstoffen ist ein wichtiger Faktor
Dass Vitamine, Spurenelemente und sekundäre Pflanzenstoffe das Immunsystem unterstützen, ist durch etliche Studien bereits belegt. Allerdings sollte man versuchen, auf die richtige Balance zu achten denn so haben Vitamine, Spurenelemente und sekundäre Pflanzenstoffe auch Wechselwirkungen untereinander und beeinflussen so unsere Stoffwechselprozesse.
Folgende Nährstoffe besitzen eine immunrelevante Wirkung:
| Mineralstoffe und Spurenelemente | Vitamine | essenzielle Fettsäuren | Aminosäuren |
| Zink | Pro-Vitamin A | Omega-3 Fettsäuren | essenzielle Aminosäuren |
| Selen | Vitamin A | Omega-9 Fettsäuren | Arginin |
| Jod | Folsäure (B9) | Ornithin | |
| Kupfer | Vitamin C | Cystein | |
| Eisen | Vitamin D | Glutamin | |
| Molybdän | Vitamin E |
Sekundäre Pflanzenstoffe und das Immunsystem, neue Grundlagen
Immer mehr in den Fokus treten die zu Unrecht benannten "sekundären" Pflanzenstoffe. Dies sind Stoffe welche die Pflanze benötigen, um sich gegen Feinde zu schützen oder ihnen als Farbstoff dienen. Für unsere Gesundheit spielen gerade diese Stoffe jedoch eine entscheidende Rolle denn Sie haben Einfluss auf eine Vielzahl von Stoffwechselprozessen.
Sie kommen vor allem in Obst, Gemüse, Nüssen und Hülsenfrüchten vor.
Der Kenntnisstand rund um die sekundären Pflanzenstoffe hat sich in den letzten Jahren stark gewandelt. Immer mehr Studien rund um die Wirkungsweise dieser Pflanzenstoffe werden jährlich publiziert.
Die neuen Erkenntnisse der Metabolomik unterstützen den Wert von Polyphenolen aus frischem Obst als potenzielle Gegenmaßnahmen zu trainingsinduzierten Immunveränderungen (belegt durch 4 Studien).
Sie wirken wahrscheinlich vorbeugend vor verschiedenen Krebsarten und vermitteln vaskuläre Effekte wie eine Erweiterung der Blutgefäße und eine Absenkung des Blutdrucks. Weiterhin entfalten sekundäre Pflanzenstoffe neurologische, entzündungshemmende und antibakterielle Wirkungen.
Irrtümer, was stimmt und was nicht
Vitamine und Mineralstoffe wirken sich positiv auf die Infektionsdauer aus. - BEDINGT
Generell ist diese Aussage nicht durch Studien belegt. Es gibt einige Ausnahmen wie Vitamin C, Zink und Selen bei denen die Zufuhr die Infektionsdauer reduzieren kann. Hier muss eine korrekte Dosierung und Einnahme erfolgen. Andere Nährstoffe können ebenfalls einen Einfluss haben.
Hoch dosierte Vitamine und Mineralstoffe machen mich resistenter gegen Infektionen. - FALSCH
Nein, längere Einnahme von hoch dosierten Vitaminen und Mineralstoffen kann oft mehr Schaden als Nützen. Es gibt präventive Therapien, diese müssen aber mit einem Facharzt abgesprochen werden.
Die Einnahme von Präparaten ist nötig, um eine optimale Zufuhr an Mikronährstoffen für das Immunsystem sicherzustellen. - FALSCH
Die Einnahme von Präparaten ist generell bei gesunden Menschen, welche auf eine gesunde Ernährung und Lebensweise achten nicht nötig. Der Einsatz von Ergänzungen sollte auf den individuellen Bedarf abgestimmt sein. Ausnahmen sind Vitamin D und Menschen die nach einer speziellen Diät leben resp. Konditionen vorliegen, welche die Aufnahme von Nährstoffen beeinträchtigen.
Vitamine und Mineralstoffe wirken unterstützend für mein Immunsystem. - RICHTIG
Wissenschaftlich ist eindeutig bewiesen, dass gewisse Vitamine, Mineralstoffe und Spurenelemente das Immunsystem in einer gesunden und optimalen Funktionsweise unterstützen. Eine Optimierung über den natürlichen Optimal (oder Normal-) Zustand hinaus ist jedoch nicht möglich.
Quellen
Bestandteil der Weiterbildung zum Fitness- und Sportnahrungsberater
Sport und Immunsystem - Aerzteblatt.de
Glutamine and the immune system
Burgenstein Handbuch Nährstoffe, 13. Auflage (ISBN:978-3-432-10657-1)
Effects of Acute and Chronic Exercise on Immunological Parameters
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Ernährung
The compelling link between physical activity and the body's defense system







